Web Developers in Sri Lanka: Full-Stack, Backend, and Frontend Specialists—Who Do You Need?

When you start looking for web developers in Sri Lanka, you'll quickly encounter terms like "full-stack," "frontend," and "backend." These aren't just industry jargon—they represent genuinely different skill sets and specialisations. Understanding what each means helps you hire the right peopl...
When you start looking for web developers in Sri Lanka, you'll quickly encounter terms like "full-stack," "frontend," and "backend." These aren't just industry jargon—they represent genuinely different skill sets and specialisations. Understanding what each means helps you hire the right people for your project and communicate effectively with technical teams.
This guide breaks down these specialisations, explains when you need each type, and helps you evaluate whether a developer's claimed expertise matches what your project actually requires.
The Architecture of Web Applications
Before diving into developer types, understanding basic web architecture helps everything else make sense.
Every website has two fundamental parts. The frontend (also called client-side) is everything users see and interact with directly—the visual design, buttons they click, forms they fill, animations they experience. This runs in the user's browser.
The backend (server-side) handles everything behind the scenes—storing data in databases, processing business logic, managing user authentication, communicating with external services. Users never see the backend directly, but it powers everything the frontend displays.
Full-stack developers work across both areas, while frontend and backend specialists focus on their respective domains. Each approach has merits; the right choice depends on your project's needs and scale.
Frontend Developers: Crafting User Experiences
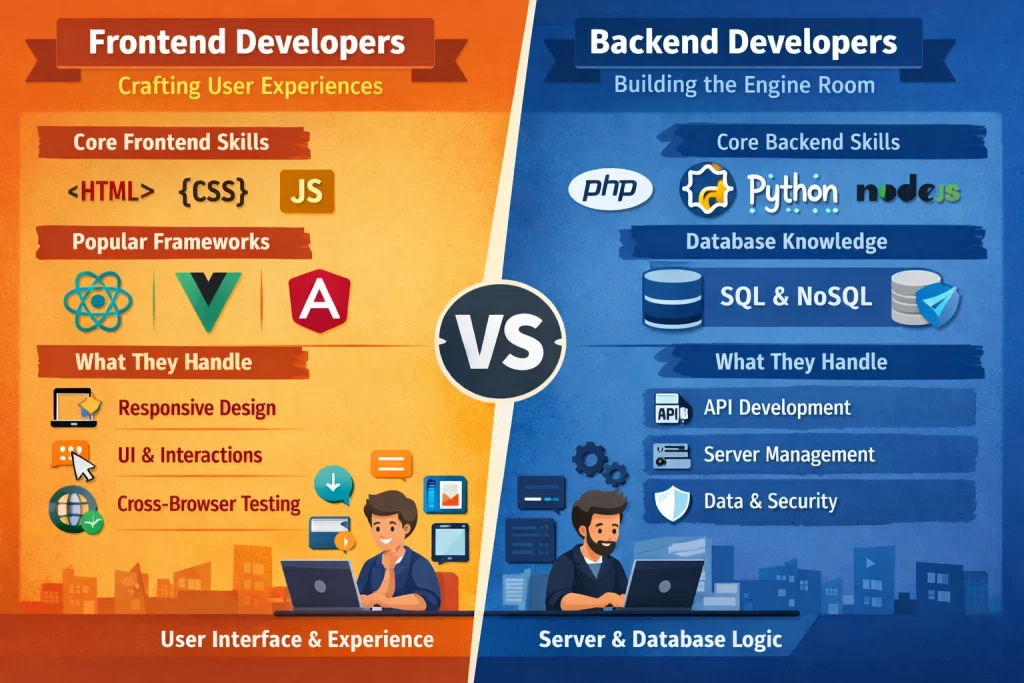
Frontend developers build what users actually see. They translate designs into working interfaces, ensuring websites look good and function smoothly across devices and browsers.
Core Frontend Skills
At minimum, frontend developers must command HTML, CSS, and JavaScript—the three foundational technologies of the web. HTML structures content, CSS styles it, and JavaScript adds interactivity and dynamic behaviour.
Modern frontend development typically involves frameworks that make building complex interfaces more manageable. React, Vue, and Angular dominate the current landscape. Each has strengths and appropriate use cases; what matters is that your developer knows at least one modern framework thoroughly.
What Frontend Developers Handle
Frontend developers are responsible for visual implementation (turning design files into working web pages), responsive design (ensuring sites work across screen sizes), user interactions (buttons, forms, animations, navigation), performance optimization (keeping the frontend fast), and browser compatibility (consistent experience across different browsers).
When You Need Frontend Specialists
Consider dedicated frontend specialists when your project involves complex user interfaces with significant interactivity, when visual polish and user experience are paramount, when performance on the client side is critical, or when you have separate backend resources already.
Evaluating Frontend Skills
When assessing frontend developers, ask about their framework experience, examine their portfolio for responsive design implementation, test their live projects on your phone, and ask how they approach performance optimization. Good frontend developers speak knowledgeably about cross-browser testing, CSS architecture, and accessibility.
Backend Developers: Building the Engine Room
Backend developers create the systems that power websites without ever being seen by users. They work with servers, databases, and application logic.
Core Backend Skills
Backend development requires proficiency in server-side languages—PHP, Python, Node.js, Ruby, Java, or others. Most backend developers specialize in one or two languages and their associated frameworks (Laravel for PHP, Django for Python, Express for Node.js, and so on).
Database knowledge is essential. This includes understanding both relational databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL) and sometimes NoSQL options (MongoDB, Redis). Knowing when to use which type and how to design efficient database structures distinguishes strong backend developers.
What Backend Developers Handle
Backend responsibilities include database design and management, API development (how frontend communicates with backend), user authentication and authorisation, server configuration and deployment, third-party integrations (payment processors, external APIs, services), and business logic implementation (the rules that govern your application's behaviour).
When You Need Backend Specialists
Backend specialists become important when your project involves complex data handling or business logic, when you're building systems that need to integrate with other software, when security is particularly critical (financial transactions, sensitive data), or when you need custom functionality that can't be achieved with existing solutions.
Evaluating Backend Skills
Ask about database experience and design philosophy. Discuss how they handle security considerations. Inquire about their experience with APIs and third-party integrations. Good backend developers talk comfortably about scalability, performance optimization, and error handling.
Full-Stack Developers: The Generalists

Full-stack developers work competently across both frontend and backend. They can build complete applications independently, handling everything from database design to user interface.
The Reality of Full-Stack
Here's an honest truth: no one masters everything. The term "full-stack" sometimes gets overused. A truly excellent frontend developer with solid backend skills might claim full-stack status, as might an excellent backend developer with adequate frontend abilities.
This isn't necessarily problematic—most projects don't require world-class expertise in every area. What matters is whether a developer's actual skill distribution matches your project's demands.
When Full-Stack Makes Sense
Full-stack developers are ideal for small to medium projects where hiring separate specialists isn't practical, for startups needing versatile team members who can handle various tasks, for rapid prototyping where one person building quickly beats coordinating multiple specialists, and for projects with balanced complexity across frontend and backend.
A web development company in Sri Lanka might employ full-stack developers for smaller projects while assembling specialist teams for larger, more complex work.
Evaluating Full-Stack Claims
When someone claims full-stack capability, probe both areas. Ask about specific frontend frameworks and backend technologies. Request portfolio examples showing both aspects. Try to understand where their strengths truly lie—knowing this helps you leverage their abilities appropriately.
Matching Developers to Your Project
Different project types call for different team compositions:
- Simple brochure websites often need a single full-stack developer or even just a frontend developer working with existing CMS platforms
- E-commerce sites with standard platforms (WooCommerce, Shopify) might need full-stack developers familiar with those ecosystems
- Custom web applications with complex functionality typically benefit from dedicated frontend and backend specialists
- Projects with heavy data processing or integration requirements need strong backend focus
- Projects prioritising exceptional user experience warrant frontend specialisation
Team Structures That Work
For many Sri Lankan business projects, you'll encounter these common team structures:
Solo Full-Stack
One developer handles everything. This works well for straightforward projects, offers simpler communication, and costs less. However, you depend entirely on one person's availability and abilities, and complex projects may exceed what one person can handle well.
Designer Plus Developer
A designer creates the visual design, and a full-stack developer implements it. This is common for small to medium projects where design matters but technical complexity is moderate.
Specialist Teams
Larger projects might involve dedicated frontend developers, backend developers, designers, and project managers. This brings deeper expertise to each area but requires more coordination and higher budgets.
Agency Teams
Working with a web design company in Sri Lanka often means accessing whatever combination of specialists your project needs. Agencies handle team composition internally, letting you focus on business requirements rather than technical staffing.
Beyond Technical Skills
Technical categorisation matters, but other factors affect project success:
Communication Abilities
Developers who can explain technical concepts clearly, understand business requirements, and collaborate effectively often deliver better results than more technically brilliant but less communicative alternatives.
Problem-Solving Approach
Web development constantly presents unexpected challenges. How developers approach problems—whether they troubleshoot systematically, research solutions, and persist through difficulties—matters as much as their starting knowledge.
Learning Orientation
Technology evolves rapidly. Developers who actively learn, stay current with their fields, and adapt to new tools and practices remain valuable over time. Ask about recent technologies they've learned or courses they've taken.
Working Effectively With Different Developer Types
Your role changes somewhat depending on who you're working with:
With frontend developers, provide clear design specifications, understand that visual implementation involves decisions about responsive behavior and interactions, and give feedback on user experience issues specifically.
With backend developers, focus on explaining business logic requirements clearly, provide access to any systems they need to integrate with, and understand that much of their work isn't visible in the interface.
With full-stack developers, communicate about the complete picture, understand they're juggling multiple concerns, and be patient when context-switching between frontend and backend work takes time.
Making Your Decision
Start by honestly assessing your project's actual requirements. Where does complexity really lie? Is it in the user interface, the backend systems, or balanced across both?
Consider your budget and timeline. Specialist teams deliver depth but cost more and take longer to coordinate. Full-stack developers offer efficiency but may lack deep expertise in specific areas.
Think about ongoing needs. If your site will need regular modifications, who will do them? Does that influence your initial hiring decisions?
The web development market in Sri Lanka includes talented professionals across all these specialisations. Whether you need a versatile full-stack developer, a dedicated frontend craftsperson, or a backend architect, you can find qualified candidates. The key is matching the right type of expertise to your project's genuine needs rather than either over-specifying or under-resourcing your requirements.
Related Articles

The Best Web Design Companies in Sri Lanka in 2026: Reviews, Ratings, and Real Client Feedback Analysis
Client reviews and ratings offer invaluable perspective when selecting a web design partner, revealing experiences that portfolios and capabilities presentations cannot convey. However, the review landscape has grown increasingly complex, with fake reviews, selective testimonials, and rating manipu...

What Makes the Best Web Design Companies in Sri Lanka: Metrics That Matter (Conversion Rate, Load Speed, User Experience)
Subjective assessments of web design quality often lead businesses astray. A website might look stunning to your eyes yet fail to convert visitors into customers. Another site might seem plain but consistently outperform competitors in generating leads and sales. The best web design companies under...
Best Web Design Companies in Sri Lanka: Awards, Certifications, and What They Actually Mean for Your Project
Web design companies frequently display awards, certifications, and recognition badges throughout their websites and proposals. These credentials promise quality assurance and industry standing, but their actual significance varies enormously. Some certifications indicate genuine expertise validate...

Web Design Companies in Sri Lanka: Real Results from Transformation Projects Across Industries
Portfolio galleries and capability claims only tell part of the story when evaluating web design companies. The real measure of a design partner's value lies in the business outcomes they help clients achieve. Transformation projects demonstrate how professional web design converts struggling onlin...